(HTS_TST) (including HTS_TST_POS) Number of individuals who received HIV Testing Services (HTS) and received their test results
Export Indicator
This indicator is intended to monitor trends in the uptake of HTS (regardless of the service delivery modality and population group) within a country.
Number of individuals who received HIV Testing Services (HTS) and received their test results
N/A
How to collect:
Existing HTS registers, log books, and reporting forms already in use to capture HTS can be revised to include the updated disaggregation categories. Examples of data collection forms include client intake forms, activity report forms, or health registers such as HTS registers, health information systems and non-governmental organization records. Data for the numerator should be generated by counting the total number of individuals who received HTS and their test results.
Note: Although several other MER indicators (see below) may report on the HIV status of individuals, actual testing of individuals must be reported under HTS_TST. Thus, any persons who are newly tested as part of the programs linked to the indicators listed below (i.e., PMTCT, TB, VMMC, Prevention services) must be reported under one of the HTS_TST modalities, unless otherwise indicated below.
- PMTCT_STAT (data from PMTCT_STAT auto-populates to HTS_TST PMTCT ANC1-Only modality)
- TB_STAT (data from TB_STAT auto-populates to HTS_TST TB modality)
VMMC_CIRC (data from VMMC_CIRC auto-populates to HTS_TST VMMC modality)
HTS_INDEX (data from HTS_INDEX auto-populates to HTS_TST Index modality)
PrEP_CURR
PP_PREV
KP_PREV
OVC_HIVSTAT
Importantly, if a site does not report on TB_STAT, VMMC_CIRC, or PMTCT_STAT, any HIV testing conducted in locations related to VMMC, PMTCT or TB should be reported under the ‘Other PITC’ modality of HTS_TST.
For an individual to be counted under this indicator, that individual’s HIV diagnosis must be confirmed using a nationally validated testing algorithm. For example, an HIV-positive rapid HIV test performed at the community- or facility- level must be confirmed with a second test, which may be performed at the same site or at a different facility. If the confirmatory test is performed at a different facility, then this may entail follow-up by implementing partners to confirm the diagnosis before reporting on this indicator. The implementing partner who first identified and tested the individual should report on HTS_TST under the appropriate modality; however, that implementing partner must ensure that the diagnosis of the individual tested is confirmed. Only a confirmed diagnosis (positive or negative) counts under HTS_TST regardless of the modality used for reporting. Similarly, simply only confirming the diagnosis of an individual who has already been tested (as per the national testing algorithm) does not fulfill the requirements for reporting on HTS_TST regardless of the modality used.
For children <1, only if serologic tests are used for diagnostic purposes should they be reported under HTS_INDEX. Serologic tests for screening infants should be excluded (including tests to look for HIV exposure at age 9 months or another time point). For example, if the partner/program uses serologic-based testing to confirm absence of HIV infection in infants <1-year-old who have not breastfed for at least 3 months prior to testing, you may use the HTS_INDEX <1 disaggregate to report negative diagnostic results for such cases. However, since diagnosis of HIV infection in infants is based on virologic and not serologic tests, the general expectation is not to see results in the “< 1” disaggregate of the HTS_INDEX indicator. HIV virologic testing of HIV-exposed infants should be counted under PMTCT_EID and PMTCT_HEI_POS.
Retesting for verification of HIV positive status before or at antiretroviral (ART) initiation should not be counted under HTS_TST since testing of this individual will have already been counted at the point of the initial diagnosis. Retesting for verification is primarily done as a quality assurance activity to avoid misdiagnosis and to ensure those initiated on ART are indeed HIV positive. Therefore, retesting for verification should only be performed for persons who have received an HIV diagnosis but have not yet been initiated on ART. While retesting for verification should not be recorded as HTS_TST or HTS_TST_POS, these data should nevertheless be tracked and rates of discordancy monitored.
Key Populations (KPs):
Provision of information (tested, tested positive, tested negative) on KPs (FSW, MSM, Transgender people, PWID, and people in prisons and other closed settings) who were tested and received their results should be reported under the KP disaggregates. However, the KP disaggregate is NOT an HTS_TST modality. All KP testing should be reported under the appropriate modality. For example, a community site keeps secure and safe records of all key populations tested at that site. This community site has determined it can report on the KP disaggregate in a safe and confidential way. Of the 100 individuals KPs who were tested and received their results (including confirmation of diagnosis) at this site, the community site reports 100 under the appropriate modality (in this case, VCT) AND reports 100 under the KP disaggregate.
See Appendix A: Key Population Classification Document, to inform identification of key populations at HTS service delivery. However, reporting of key population disaggregation should be consistent with what is described under the KP_PREV “How to review for data quality” section on mutual exclusivity of an individual who falls under multiple key population categories (e.g., FSW who injects drugs). In such instances, the individual should only be reported in ONE key population disaggregation category to avoid double-counting.
Note: Both key population-specific and clinical partners should complete these disaggregations, but only if it is safe to maintain these files and report. Age and sex data on key populations receiving tests for recent infection will not be reported. Please refer to the KP_PREV indicator reference sheets for more information on working with KPs.
The first priority of data collection and reporting of HTS among key populations must be to do no harm. These data must be managed confidentially to ensure the identities of individuals are protected and to prevent further stigma and discrimination of key populations.
Note the misalignment of reporting frequency between HTS_TST [quarterly] and KP_PREV [semi-annually] and the differences in the process of de-duplication of individuals (HTS_TST is de-duplicated within the quarter, whereas KP_PREV is de-duplicated within the fiscal year). For example, if a KP is reached and tested more than once within the fiscal year, s/he will only be counted once under KP_PREV but could be counted multiple times under HTS_TST KP disaggregation during same the fiscal year if the KP was tested multiple times in different quarters. However, if a KP is tested multiple times within the same quarter, s/he should be deduplicated (i.e., only be counted once in the quarter). Please be cognizant of such limitations when interpreting KP_PREV, HTS_TST, and HTS_TST_POS cascade data by key populations.
Data Systems and Tools
When developing or modifying existing monitoring and evaluation systems and tools to collect and report on this indicator, the following information should be considered (* designates data elements that are required for HTS_TST reporting in DATIM):
- This indicator counts the number of individuals tested not the number of tests conducted. All efforts should be made to ensure data are collected on individuals tested vs. number of tests conducted through de-duplication. Within HTS registers, collecting data on the following variables should be considered to help in these efforts:
- Retesting status: new tester, re-tester (i.e., tested in the last 3 months), retesting to verify an HIV-positive diagnosis before ART initiation
- HIV testing services - *HIV test results, date of HIV test, receipt of HIV test results, previously tested during the reporting period
- Demographic - Client’s Unique ID, name, *sex, and *age at time of HTS services
- Date HIV-positive individual was linked to treatment
- Site - *site name and ID, district, region, province, and *service delivery modality
- Using unique identifiers for individuals is one way to account for retesting and avoid double reporting if electronic systems are available to easily link data through these unique identifiers. Another approach is to record information about prior testing on the HTS client register.
- For an individual to be counted under HTS_TST, their HIV diagnosis must be confirmed using a nationally validated testing algorithm. For example, an HIV-positive rapid HIV test performed at the community- or facility- level must be confirmed with a second test, which may be performed at the same site or at a different facility. If the confirmatory test is performed at a different facility, then this may entail follow-up by implementing partners to confirm the diagnosis before reporting on this indicator. The implementing partner who first identified and tested the individual should report on HTST_TST under the appropriate modality; however, that implementing partner must ensure that the diagnosis of the individual tested is confirmed. That is, only a confirmed diagnosis (positive or negative) counts under HTS_TST regardless of the modality used for reporting. Similarly, simply only confirming the diagnosis of an individual who has already been tested (as per the national testing algorithm) does not fulfill the requirements for reporting on HTS_TST regardless of the modality used.
- Note: Retesting for verification of HIV positive status before or at antiretroviral (ART) treatment initiation is only done for persons who have already been diagnosed HIV- positive as per the national HIV testing guidelines. All clients diagnosed HIV-positive should be retested for verification before or at ART initiation with a new specimen and preferably a second operator using the same national HIV testing strategy. Retesting for verification is primarily done as a quality assurance activity to avoid misdiagnosis and to ensure those initiated on ART and treatment services are indeed HIV positive. Thus, HIV testing conducted to verify status should not be counted under HTS_TST, since their initial HIV diagnosis will have already been counted at the point of the initial receipt of the HIV diagnosis (as per the national HIV testing guidelines).
- Patient level Deduplication: adding “has patient been tested in the last 3 months” to the HTS facility and community registers can help implementing partners de-duplicate at the reporting level.
How to review for data quality:
Only one age disaggregation type is used for age/sex/test result received:
The number of individuals newly receiving ART must be disaggregated by age and sex.
Reporting level: Facility & Community
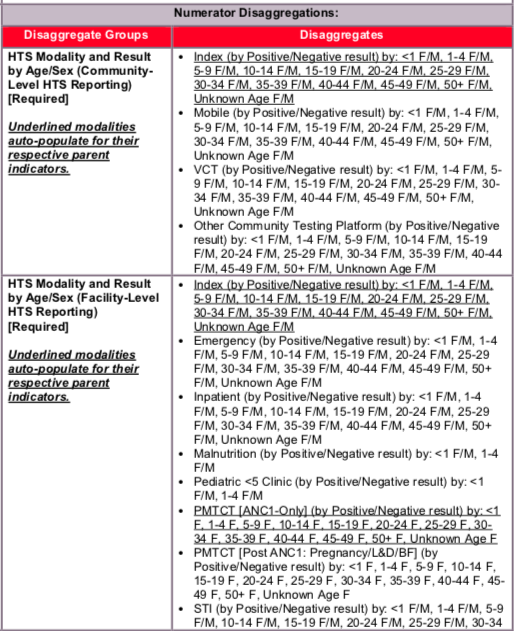
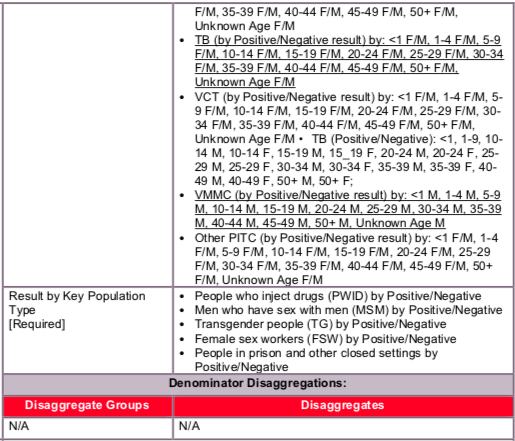
Disaggregate descriptions & definitions:
Disaggregates: Service Delivery Modality
In addition to reporting the total number of individuals tested and receiving their test results and the total type of test results received (negative, positive), HTS_TST data should be disaggregated by service delivery modality, and then also by age/sex/test result within each service delivery modality. Service delivery modalities can reflect a reason for testing (index, STI), as well as, the location/place of testing (e.g., inpatient ward, VCT drop-in center). For example, STI and Index in this context refer to a reason a person is seeking or being offered an HIV test i.e., the person suspects he/she may have an STI or the person is a contact of an index client (see modalities below for more details). In either case (STI or index), that person should be reported under either STI or index even if he/she were tested for HIV any other location or setting (inpatient, VCT, drop-in center). That is, reporting the reason for testing as either STI or Index takes precedence over all other modalities. A single person should only be counted once under any given modality.
Service delivery modalities are defined as:
Community-based testing: Applies to any testing done outside of a designated health facility. Within community-based testing, the following disaggregates are available:
- Index: Importantly, the index modality under HTS_TST will auto-populate from HTS_INDEX (see HTS_INDEX reference sheet for more information). Index testing, also referred to as partner testing/partner notification services, is an approach whereby the exposed contacts (i.e., sexual partners, biological children and anyone with whom a needle was shared) of an HIV-positive person (i.e., index client), are elicited and offered HIV testing services. That is, in this context, Index testing refers to any HIV testing of contacts of an index client (i.e., a known positive). Only the following persons count as contacts: current or past sexual partner(s), biological children /parents (if index case is child) or anyone with whom a needle was shared. Biological children reported under HTS_INDEX should only include children of an HIV-positive mother and children of male-index clients (fathers) whose biological mother is HIV-positive, deceased, or her HIV status is not known or not documented. Conversely, if the index client is the child, his/her mother should be tested, and if positive or deceased, the father should be tested as well. In this way, provision of index testing services is non-directional, whereby we are trying to follow transmission of the disease, and every newly identified positive becomes a subsequent index client from whom to elicit contacts. While testing the contacts of an index client may occur in mobile, VCT or other community testing venue, this testing should be reported under HTS_INDEX. That is, if an individual could be reported under both HTS_INDEX and another HTS_TST modality, that individual should only be reported once under HTS_INDEX. Again, the index modality under HTS_TST will auto-populate from HTS_INDEX (see HTS_INDEX reference sheet for more information).
- Mobile: Testing in Mobile ad hoc or temporary testing locations, such as community centers, schools, workplaces, and includes testing in mobile unit such as tents and vans. Testing related to VMMC services is not included here and should be reported under facility based VMMC modality.
- VCT (Voluntary Counseling and Testing): Includes testing conducted in standalone VCT center that exists outside of a designated health facility (e.g., drop-in-center, wellness clinic where HTS services are provided, testing sites aimed at key populations, etc.).
- Other community platforms: Includes all community-based modalities not captured above (e.g., ad hoc testing campaign that does not satisfy the mobile testing definition) and community-based OVC testing) should be entered under this modality.
Facility-based testing: Applies to any testing occurring inside a designated health facility. Within the facility-based testing, the following disaggregates are available:
- Index: Importantly, the index modality under HTS_TST will auto-populate from HTS_INDEX (see HTS_INDEX reference sheet for more information). Index testing, also referred to as partner testing/partner notification services, is an approach whereby the exposed contacts (i.e., sexual partners, biological children and anyone with whom a needle was shared) of an HIV-positive person (i.e., index client), are elicited and offered HIV testing services. That is, in this context, Index testing refers to any HIV testing of contacts of an index client (i.e., a known positive). Only the following persons count as contacts: current or past sexual partner(s), biological children /parents (if index case is child) or anyone with whom a needle was shared. Biological children reported under HTS_INDEX should only include children of an HIV-positive mother and children of male-index clients (fathers) whose biological mother is HIV-positive, deceased, or her HIV status is not known or not documented. Conversely, if the index client is the child, his/her mother should be tested, and if positive or deceased, the father should be tested as well. In this way, provision of index testing services is non-directional, whereby we are trying to follow transmission of the disease, and every newly identified positive becomes a subsequent index client from whom to elicit contacts. While testing the contacts of an index client may occur in mobile, VCT or other community testing venue, this testing should be reported under HTS_INDEX. That is, if an individual could be reported under both HTS_INDEX and another HTS_TST modality, that individual should only be reported once under HTS_INDEX. Again, the index modality under HTS_TST will auto-populate from HTS_INDEX (see HTS_INDEX reference sheet for more information).
- Provider Initiated Counseling and Testing (PITC):
- Emergency: Includes persons tested or seen in a designated emergency department or ward for the immediate care and treatment of an unforeseen illness or injury.
- Inpatient: Includes PITC occurring among those patients admitted in the inpatient and surgery wards.
- Malnutrition: Clinics and inpatient wards predominately dedicated to the treatment of malnourished children. While this service delivery modality may be part of either inpatient or outpatient services, if an individual could be reported under both malnutrition and another service delivery modality, report an individual only once and under malnutrition. However, the biological children of female index cases should be classified under the Index testing modality.
- Pediatric <5 Clinic: Includes PITC occurring in the pediatric <5 clinic only. This modality refers only to children tested in the <5 clinic. Children tested for any other reason should be counted under the respective modality where their testing occurred. Note that this modality does not include virologic testing, which is reported under PMTCT_EID, nor rapid HIV testing used to identify HIV exposed infants. This modality should also not include children of index cases who should be classified under the Index modality or malnourished children who should be classified under Malnutrition.
- PMTCT (ANC1 Only): Pregnant women tested at their 1st antenatal care clinic (ANC) for their current pregnancy (who are also reported under PMTCT_STAT) are reported under this modality. Refer to PMTCT_STAT reference sheet for guidelines on data collection. Individuals counted under PMTCT_STAT who already knew their status should not be reported under HTS_TST.
- PMTCT (Post ANC1: Pregnancy/L&D/BF): Includes pregnant or breastfeeding women who receive a test POST ANC1, this includes women who are tested later in pregnancy (>ANC2), during labor & delivery (L&D), and while breastfeeding.
- STI: Includes persons seen in a designated STI clinic as well as patients seen in the OPD for STI symptoms. This includes suspect and confirmed STI cases. HIV testing may take place in an STI clinic, an OPD, a co-located VCT or other setting. However, if the reason for the HIV testing is the individual is either a suspect or confirmed STI case, then the test should be reported under the STI modality.
- TB: Includes persons referred for HIV testing because they are a confirmed TB case. Refer to TB_STAT for guidelines on data collection for TB. Individuals counted under TB_STAT who already knew their status should not be reported under HTS_TST.
- Other PITC: This includes any other provider-initiated testing and counseling that is not captured in one of the other testing modalities listed above. For reporting purposes, this includes testing of patients triaged to other clinics within the OPD that see patients for routine/chronic care (i.e., eye, dental, dermatology, diabetes, etc.). This does not include patients seen in the OPD for emergency care or an STI. Those patients should be classified under the emergency and STI modalities, respectively.
- VMMC: This modality includes HIV testing for males conducted as part of VMMC programs in both facility and mobile outreach programs. Testing is recommended through the VMMC program, although not mandatory. Refer to VMMC_CIRC for guidelines on data collection for VMMC.
- VCT: Refers to a clinic specifically intended for HIV testing services that is co-located within a broader health care facility. This data can typically be found in the VCT register. This should not include testing of patients referred by providers from other clinical services within the facility (TB, ANC, Inpatient, emergency, etc.). Even though the actual test may be administered in the VCT clinic, report those individuals under the serviced delivery modality from which they were referred. This modality should also not include testing of exposed partners and exposed family members of an index case, who should be reported under the Index disaggregate.
The numerator captures the number of individuals who received HIV Testing Services (HTS) and received their test results. At a minimum, this means the person was tested for HIV and received their HIV test results
Indicator changes (MER 2.0 v2.3 to v2.4): None
PEPFAR Support definition:
Standard definitions of DSD and TA-SDI apply.
For HTS services, direct service delivery includes: ongoing procurement of critical HTS related commodities such as rapid HIV test kits or requisite materials (lancets, capillary tubes), samples and materials for proficiency testing, other HIV diagnostic commodities, or funding for salaries of HIV testing service providers including counselors, laboratory technicians, program managers, and/or community health workers. Staff who are responsible for the completeness and quality of routine patient records (paper or electronic) can be counted here; however, staff who exclusively fulfill MOH and donor reporting requirements cannot be counted.
For HTS services, ongoing support for service delivery improvement includes: clinical mentoring/supportive supervision, HTS training, HTS guidance development, routine support of HTS M&E and reporting, or HIV test kits consumption forecasting and supply management.
Guiding narrative questions:
- Please describe and/or specify any processes or data available for determining rates of retesting (not including verification testing) of both HIV positives and negatives.
- Please describe processes/methods and/or quantify any estimation of linkage to treatment from diagnosis.
- Please describe and/or quantify (proportions retested prior to ART, concordance or discordance rates) verification testing occurring prior to ART initiation to minimize misdiagnosis.
- Please describe processes/methods for capturing new service delivery modalities (STI and Emergency) and any challenges with accurately capturing these modalities.
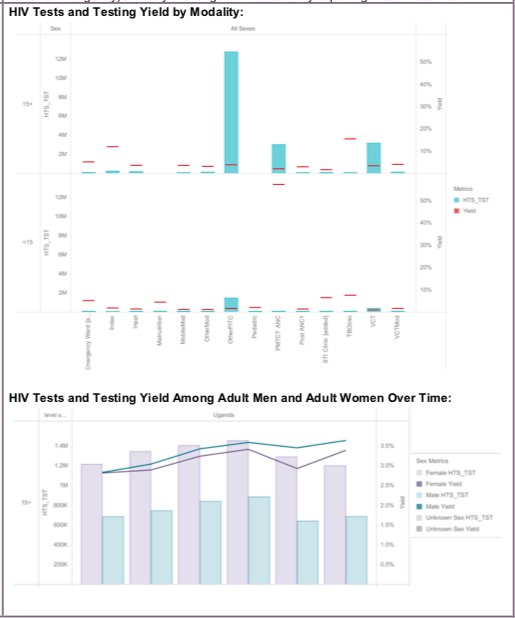
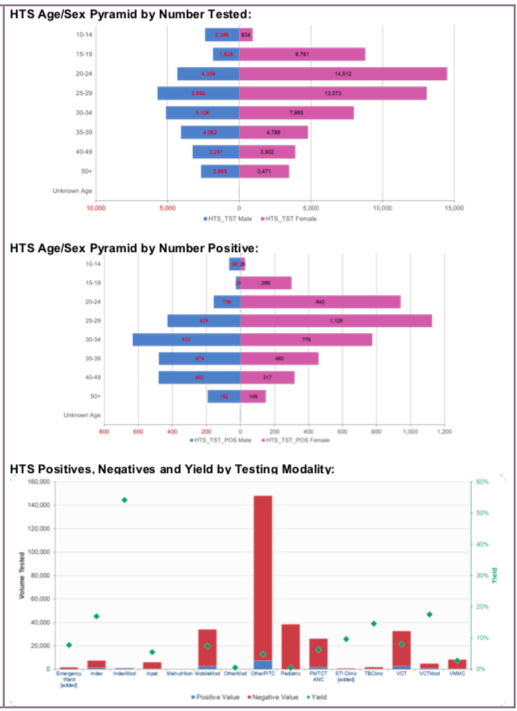
TL.2 HTS testing volume and positivity, 2020, WHO Consolidated HIV strategic information guidelines: driving impact through programme monitoring and management (https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/consolidated-hiv-strategic-information-guidelines).