(HTS_SELF) Number of individual HIV self-test kits distributed
Export Indicator
This is the first MER indicator to monitor PEPFAR programming of HIV self-testing approaches and distribution HIV self-test kits.
HIV self-testing refers to a process in which a person collects his or her own specimen (oral fluid or blood), performs an HIV test, and then interprets the results. This is often done in a private setting, either alone or with a trusted person. HIV self-testing is a screening test and requires self-testers with a reactive (preliminary positive) result to receive further testing from a trained provider using a validated national testing algorithm. HIV self-testing approaches range from unassisted self-testing (with limited or no instruction provided) to directly assisted self-testing (where a testing provider demonstrates how to use the self-test kit). Self-test kits can be distributed in various ways (i.e., by providers or outreach workers, over-the-counter, etc.). Secondary distribution of HIV self-test kits may also occur (e.g., to partners of ANC attendees, or clients of FSWs).
This indicator aims to monitor trends in the distribution of HIV self-test kits within a country at the lowest distribution point (i.e., between the distributer and the intended user(s)/recipient). The implementation of HIV self-testing programs should facilitate and enhance access to and uptake of HIV testing services for populations where HIV test uptake is low and undiagnosed HIV infection is high (i.e., men, adolescents/young adults, and key populations).
Number of individual HIV self-test kits distributed
N/A
How to calculate annual total: Sum results across quarters
How to collect:
The suggested data source is a (newly developed) HIVST (HIV self-test) register or logbook. This will minimize any potential confusion with HTS_TST data collection and reporting since HIV self-testing is only a screening test and should not be reported under HTS_TST which only includes diagnostic testing. If a standalone HIVST register or logbook is not possible, revise existing HTS registers, log books, and reporting forms already in use to include very clear labels to indicate self-testing to prevent information entered in an HTS register from being counted and reported under HTS_TST or HTS_TST_POS.
Note that one individual can receive multiple self-test kits (e.g., one for themselves and one for their partner or partners). Data for the numerator should be generated by counting the number of individual HIV self-test kits distributed and NOT the number of individuals receiving an HIV self-test kit. Number of self-test kits distributed should be captured and reported at the lowest distribution point. The lowest distribution point refers to the individual/site giving out self-test kits and capturing data for monitoring purposes. This is to prevent double counting between the various higher supply chain levels.
For example, the central warehouse distributes 500 self-test kits to an implementing partner doing outreach for KPs. The implementing partner gives their peer outreach workers a total of 50 self-test kits to give out during an outreach event. The outreach workers return from their event having given out 30 self-test kits. In this scenario, the lowest distribution point would be the outreach workers who are capturing the monitoring data. Therefore, the number of tests kits distributed would be 30. Each of these lowest distribution counts should be rolled up (aggregated) to create the numerator for this indicator.
The disaggregation by type of self-testing provides information about the proportion of test kits distributed through each model (i.e., directly assisted vs. unassisted self-testing). Further disaggregation by “number of tests distributed to a person by age/sex” (for both directly assisted and unassisted self-testing) and “test kit distributed for use by” (for unassisted self-testing) can provide information about what subpopulations are receiving HIVST kits and who the test kit is intended for use by (i.e., self, sex partner, other) in the unassisted model. The findings can support national government and PEPFAR programs to assess how efficient different distribution approaches are at reaching target populations. These data may also be useful for projecting programmatic commodities (e.g., self-test kits) and systems needs (e.g., staffing resources). It is important to note that for the purposes of this indicator, it is assumed that the tests distributed to individuals and counted in the directly assisted self-testing model are the used by individuals that received them so the disaggregation for “test kit distributed for use by” is not requested in the directly assisted model. Please refer to the example clarification below for additional details.
For example, if an 18-year-old female reports to a testing site and receives a one-on-one testing demonstration for herself – the test for herself will be reported as directly assisted and you would provide the age/sex disaggregation data for one test kit distributed in the 15- 19-year-old age band. When she leaves the clinic, she takes two additional test kits along with her: one for her sex partner and one for her friend to use at a later time. The two test kits for her sex partner and friend would be counted as unassisted. For the age/sex breakdown under unassisted, 2 tests would go in the 15-19-year-old female age band because two tests were distributed to the female in that age band. The reporting follows the distribution of the test kits and not the age/sex demographics of the end user of the self-test kit. For the “test kit distributed for use by” disaggregate, you would indicate a ‘1’ in the ‘sex partner’ disaggregate for the test she planned to distribute to her sex partner and a ‘1’ in the ‘other’ disaggregate for the test she planned to distribute to her friend.
It is understood that registers and procedures for HIVST are still relatively new in many PEPFAR countries and specific distribution methods (e.g., vending machines) may not always allow for collection of detailed data on self-test kit distribution. As such, the only required disaggregate for this indicator will be for the type of self-testing (i.e., directly- assisted vs. unassisted). In addition, age/sex demographic information for test kits distributed using the directly-assisted self-testing model will also be required as these individuals should have received an in-person HIV test kit demonstration and demographic information should be collected at that time
Note: Although not required, implementing partners should attempt to document and report information about actual use of self-test kits. This includes who used the test kit, the test result from the self-test and linkage to retesting (if result is reactive), particularly when directly assisted HIVST occurs. Methods used may include request the return of the kits or follow up calls to determine outcomes. This information can further inform whether HIVST services are reaching individuals who may be HIV-positive and if those individuals are retesting to confirm their diagnosis.
For more information on HIV self-testing, please refer to the “WHO Guidelines on HIV Self- Testing and Partner Notification” released in December 2016. To review a repository of country-specific guidance and polices related to HIV self-testing, please visit the HIV Self- Testing Research and Policy Hub.
How to review for data quality:
Data should be reviewed regularly for the purposes of program management, to monitor progress towards achieving targets, and to identify and correct any data quality issues. For example, the number of test kits distributed should not be greater than the number of test kits a provider allocated during the reporting period. Pay careful attention to the number of HIVST kits distributed at pharmacies and online.
Implementing partners should review their data to ensure that HTS_SELF is not reported under HTS_TST (or HTS_TST_POS) results. Furthermore, data should be reviewed to ensure the numerator does not include the number of HIV self-tests performed or used, nor does it reflect a definitive diagnosis (which would be reported under HTS_TST).
The “directly-assisted” disaggregate should be reviewed to see if additional information was collected related to: 1) test result (negative or reactive) and 2) linkage for repeat testing to confirm a reactive self-test result. While not required for this indicator, this information should be collected by implementing partners as part of routine program monitoring.
Reporting level: Facility & Community
Reporting frequency: Quarterly
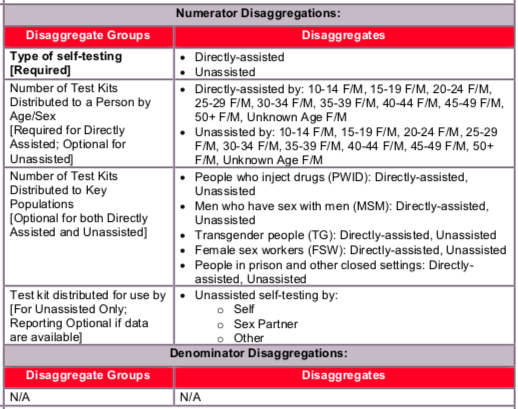
Disaggregate descriptions & definitions:
Type of self-testing:
- Directly assisted HIVST refers to trained providers or peers giving individuals an in- person demonstration before or during HIVST of how to perform the test and interpret the test result (WHO, 2016).
- Unassisted HIVST refers to when individuals self-test for HIV and only use an HIVST kit with manufacturer-provided instructions for use. In addition to reporting the total number of HIV self-test kits distributed to individuals, the HTS_SELF indicator includes several disaggregates to characterize aspects of distribution (WHO, 2016).
Test kit distributed for use by [For Unassisted Only; Reporting]:
- Self: Individual that HIV self-test kit was distributed to intends to use the test kit on him- or herself.
- Sex Partner: Individual that HIV self-test kit was distributed to plans to further distribute the self-test kit for use on his or her sexual partner(s).
- Other: Individual that HIV self-test kit was distributed to plans to further distribute the test kit to an individual that is not themselves or one of their sex partners (e.g., relative, friend)
This indicator aims to monitor trends in the distribution of HIV self-test kits within a country at the lowest distribution point.
Indicator changes (MER 2.0 v2.3 to v2.4): None
PEPFAR-support definition:
Standard definition of DSD and TA-SDI used.
Provision of key staff or commodities for the distribution of HIVST kits includes: ongoing procurement of HIVST kits or funding for salaries of providers who distribute or directly assist with HIVST including counselors, laboratory technicians, program managers, and community health workers. Staff who are responsible for the completeness and quality of routine patient records (paper or electronic) can be counted here; however, staff who exclusively fulfill MOH and donor reporting requirements cannot be counted.
For HIVST, ongoing support for service delivery improvement includes: clinical mentoring/supportive supervision, HIVST training, HIVST guidance development, site level QI/QA, routine support of HIVST M&E and reporting, or HIVST kit consumption forecasting and supply management.
Guiding narrative questions:
- Describe the process/methods and challenges for tracking distribution of test kits.
- Describe process/methods and challenges for tracking use of self-test kits.
- Describe process/methods and challenges for tracking linkage of individuals for repeat testing to confirm a reactive self-test result.